With the French subsidiary Therenva, Ziehm Imaging is shaping the future of mobile image fusion. Headquartered in Rennes, Therenva is a leading developer of 3D planning software for cardiovascular interventions. In his daily routine, Prof. Dr. Adrien Kaladji uses the combination of mobile C‑arms and hardware as well as software packages for case planning and intraoperative navigation.
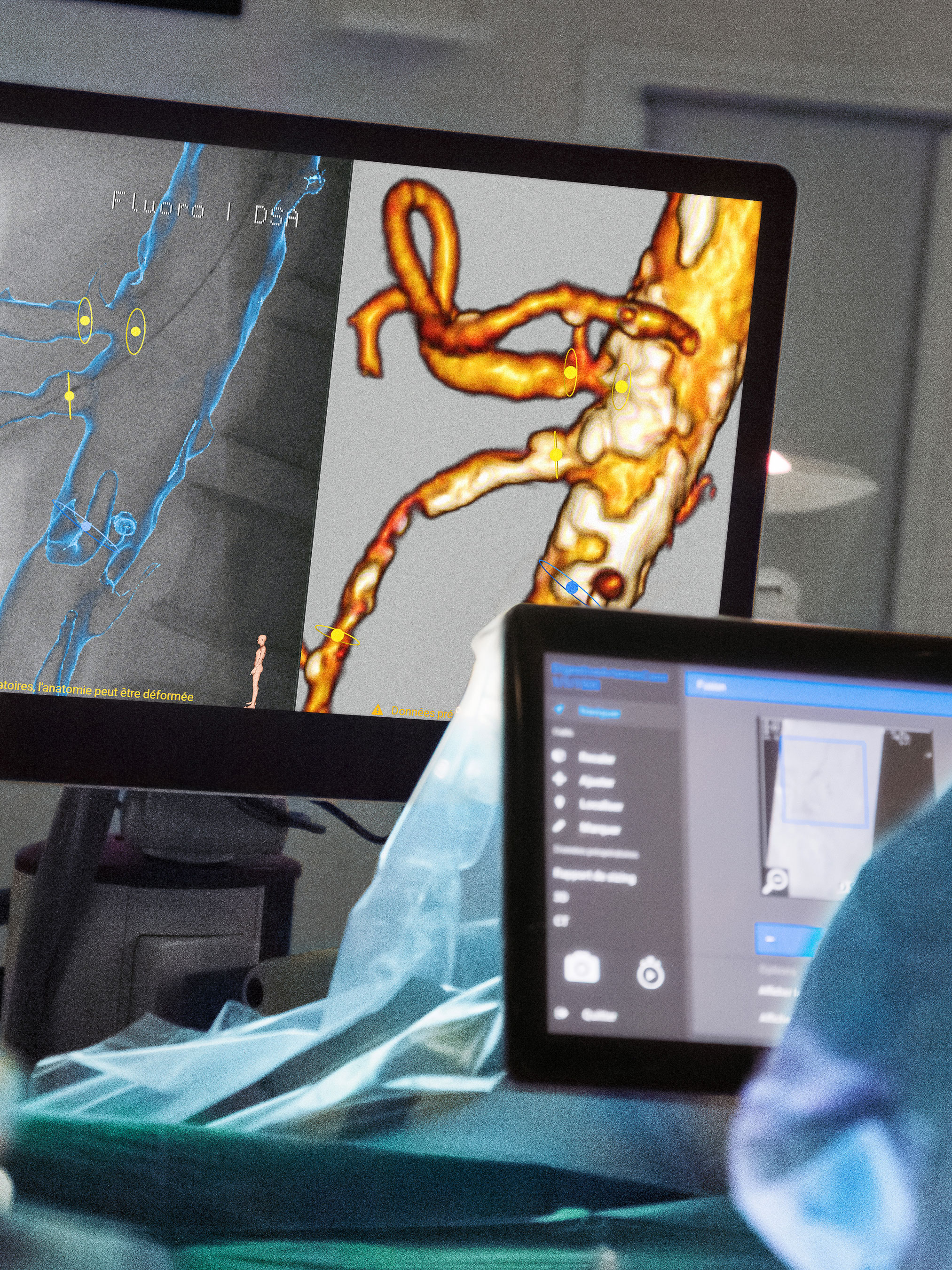
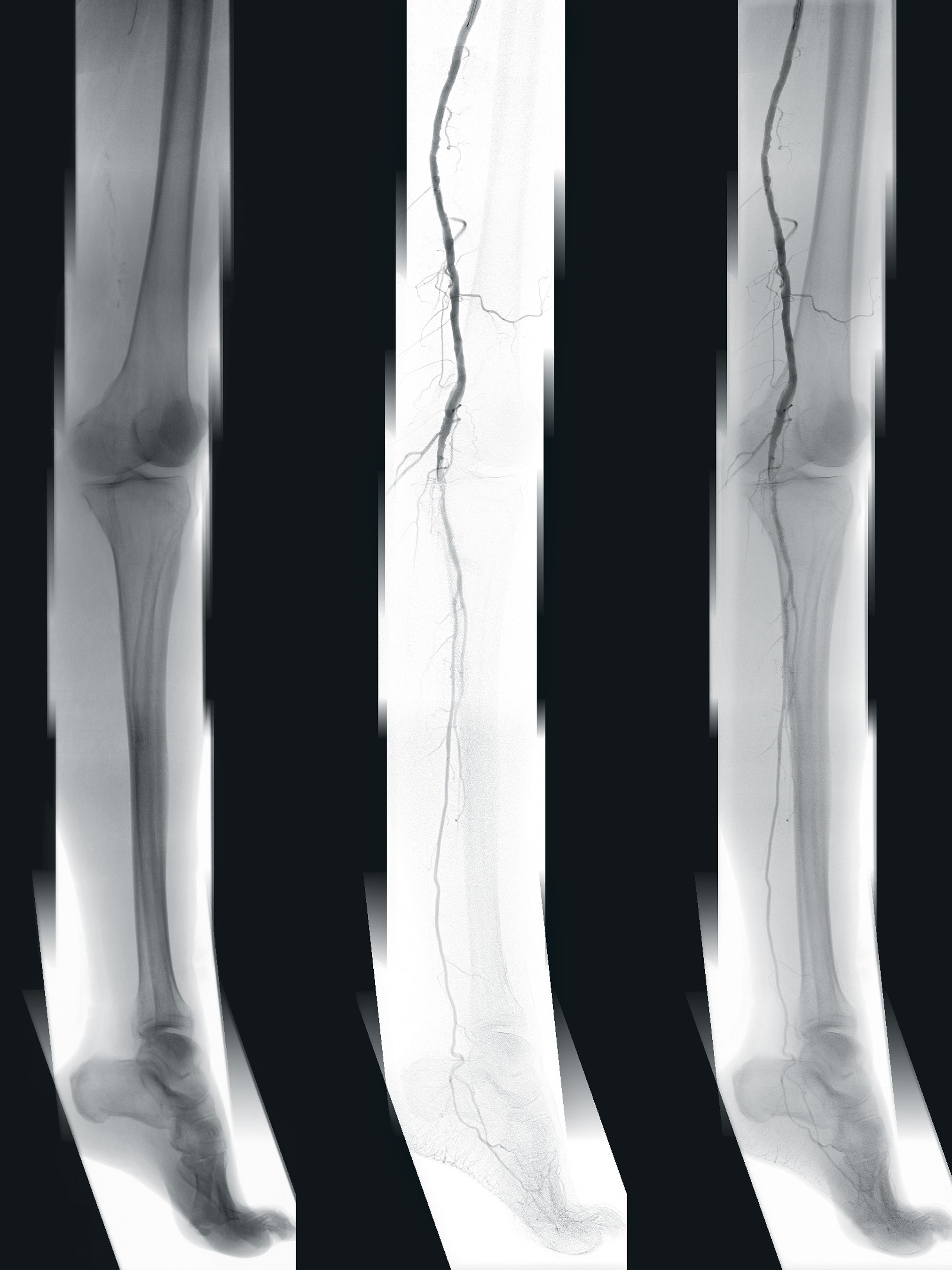
The unique 3D planning software EndoSize1 supports Prof. Dr. Kaladji in his routine to this day. It enables the digital planning of minimally invasive vascular surgeries on a desktop computer or laptop. The plans are then stored in the hospital’s imaging and communication system or on a USB stick for later use in the OR. In addition to determining the appropriate stents and C-arm angles for relevant imaging during surgery, the CT image acquired for diagnostic purposes can also be processed by the software. For example, the areas that need repair in the vessels, such as aneurysms, stenoses, and blockages can be marked.
Adjacent vessel outlets can also be registered so that they are not blocked with stents during surrgery. These markings support the surgeon during the operation because the processed image, including the markings, can be superimposed on the live image taken by the C-arm with the aid of the EndoNaut2 of the mobile Therenva system. It shows the physician where in the vessel the intervention is to take place. According to Prof. Dr. Kaladji, this procedure has advantages above all for the patient: “You have planned the intervention in advance. This helps especially with FEVAR and EVAR interventions. Without this option, we had to use more contrast agent and needed more images, which also led to a higher dose. At that time, for example, we didn’t know which perspective would produce the best view of the problem area. We had to improvise a lot more.”

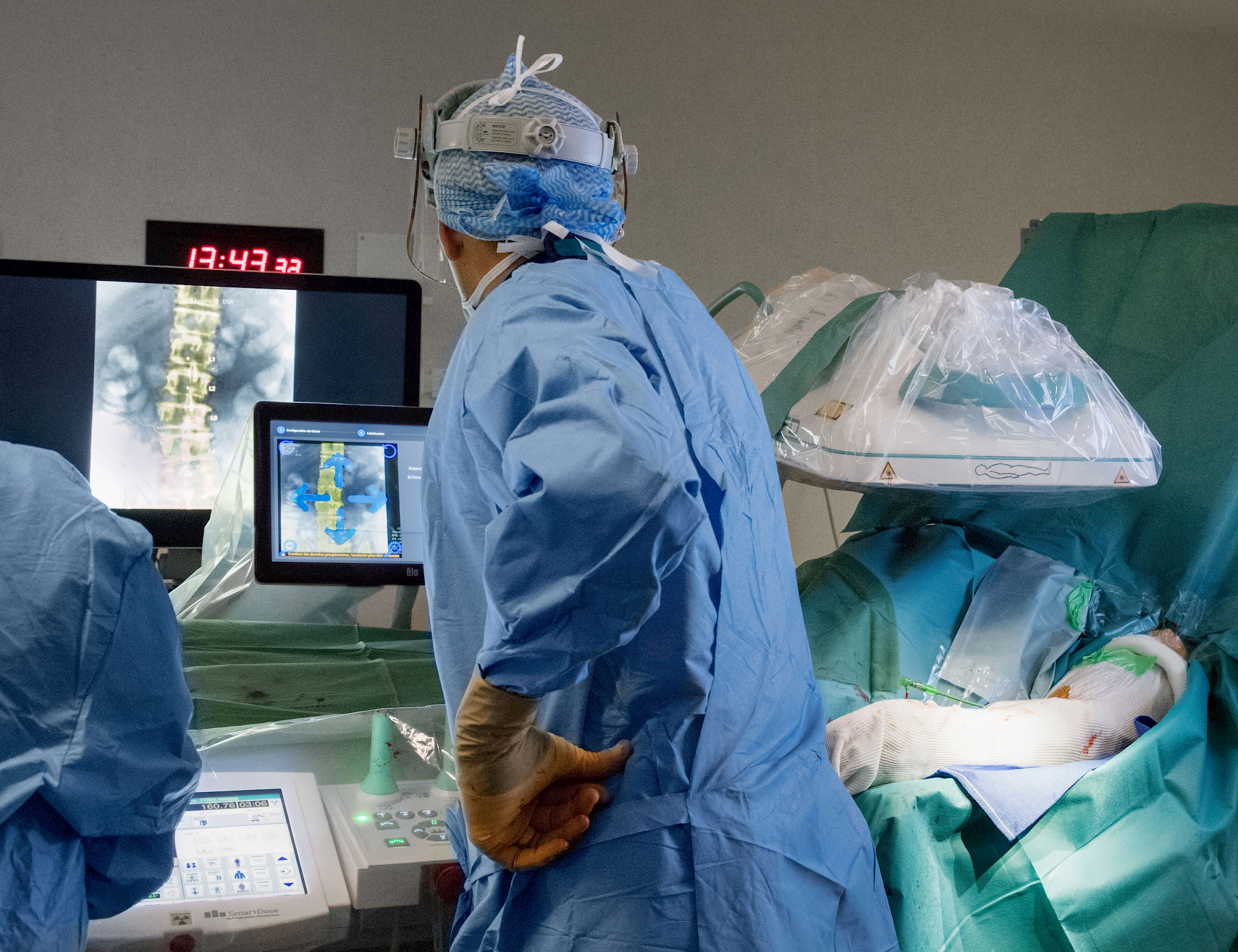
Today, Prof. Dr. Kaladji heads the Department of Thoracic, Cardiac and Vascular Surgery at the Center for Cardiology and Pneumology at the University Hospital in Rennes with his colleagues. More than 2,000 vascular surgeries are performed there each year. Prof. Dr. Kaladji is an internationally-recognized expert in his field. The vascular surgeon operates as precisely and carefully as possible during each operation. And intraoperative imaging helps him.
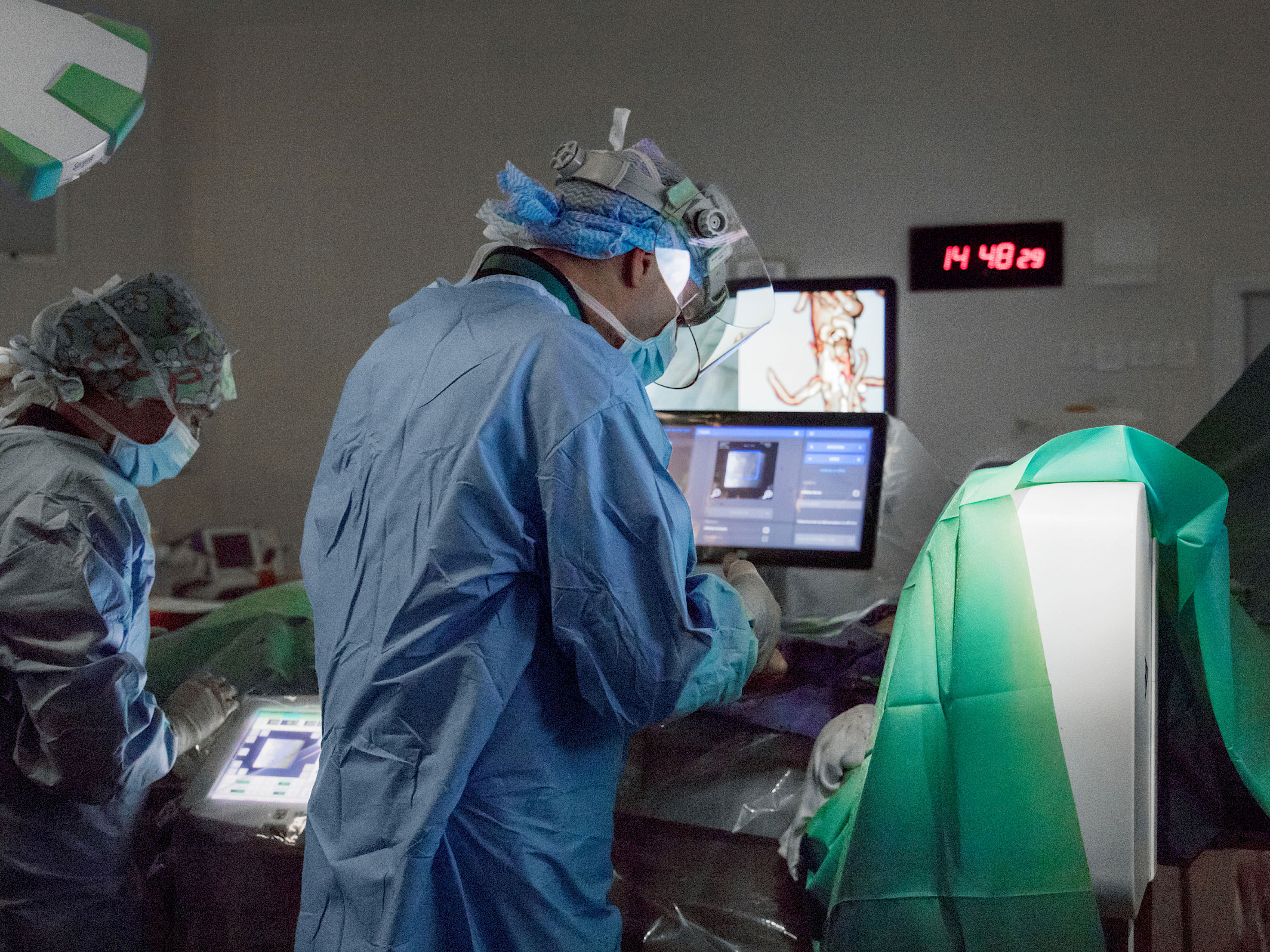
For this, he uses the Ziehm Vision RFD Hybrid Edition3 CMOSline4 – its images impressed him from the beginning. Prof. Dr. Kaladji sees the significantly lower investment costs compared to a fixed system, and in the ease of operation as additional meaningful advantages of the mobile C‑arm. The system just needs to be connected to the power supply in the OR and is immediately ready to use. In addition, its mobility allows the OR setup to be changed during the procedure, if necessary, thereby enabling more flexibility in the OR workflow than a permanently installed system. He uses the C‑arm with Therenva’s EndoSize and EndoNaut systems. This enables the transferal of the pre-planned surgical data to the live image acquired with the C‑arm. In addition, real-time visualization of the instruments can be overlaid on the current patient images. The decisive factor is always the image quality of the fluoroscopic images of the C‑arm. The sharper the images and the more clearly the contours are displayed, the better the results delivered by the image fusion of the C‑arm 2D images with the EndoSize 3D images.
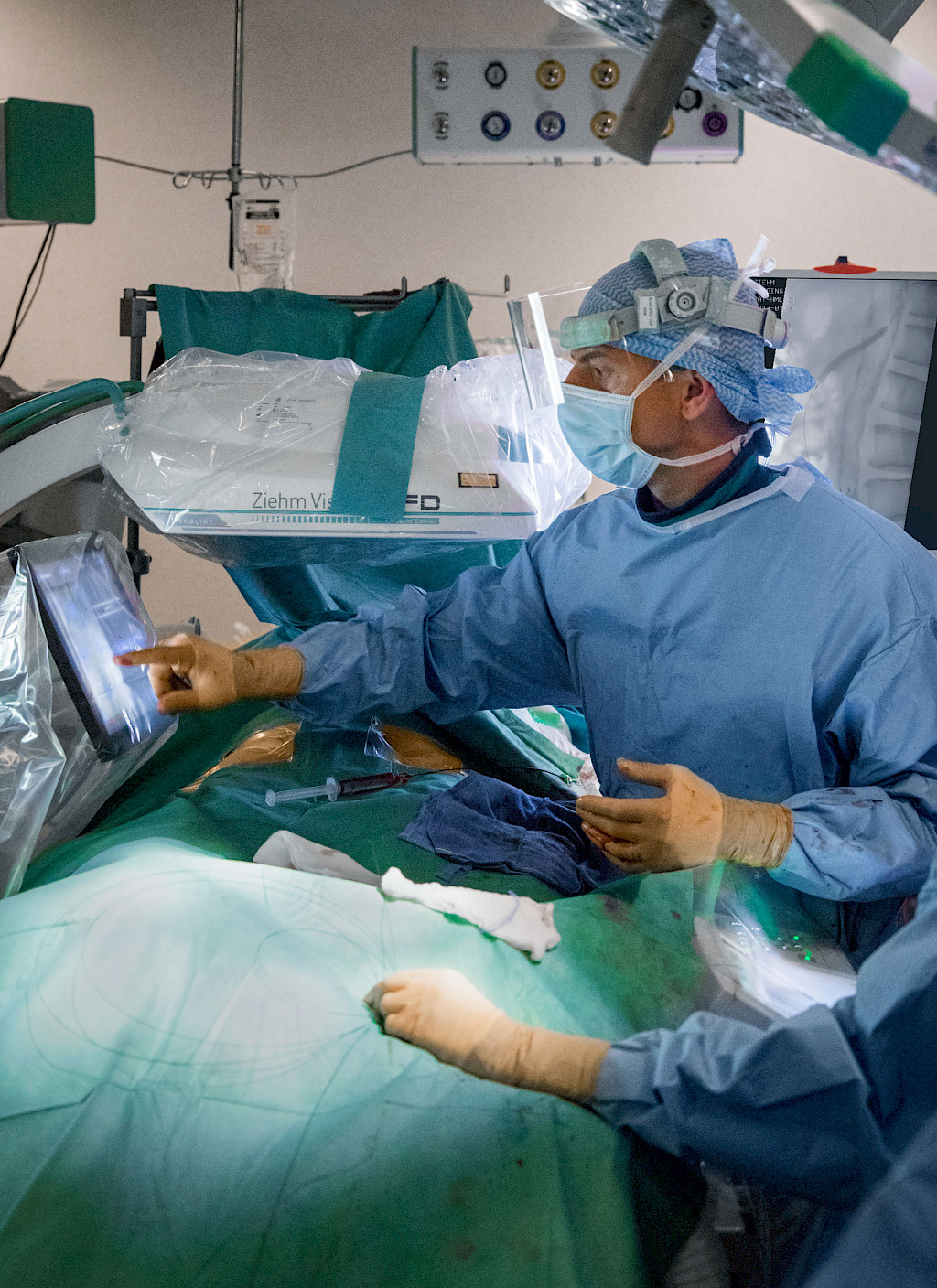
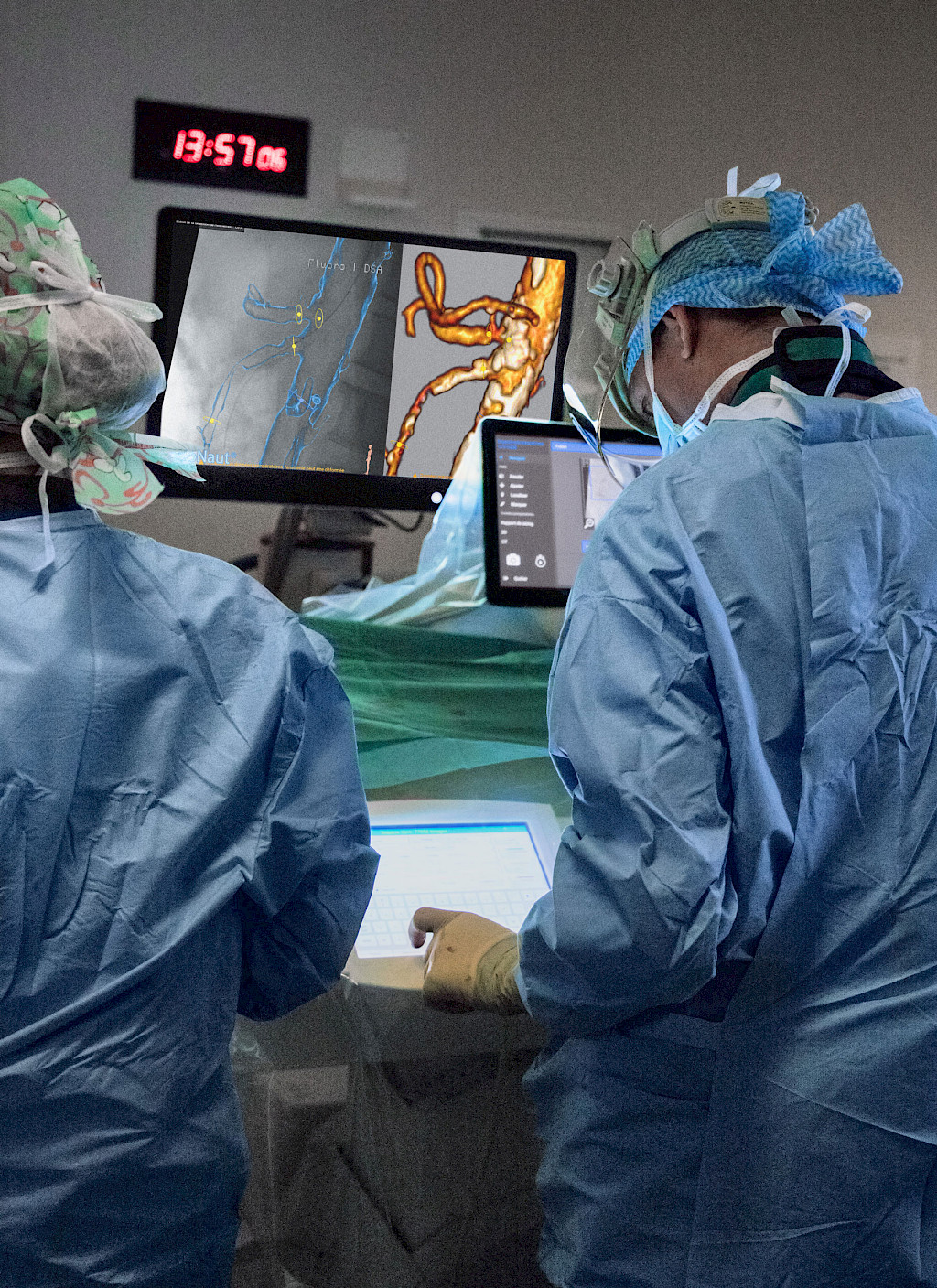
Today, Prof. Dr. Kaladji and his team are scheduled to revascularize a side branch of an aorta. The opening of such vascular occlusions is one of the standard procedures that Prof. Dr. Kaladji has been performing at the University Hospital in Rennes for more than ten years. After entering the operating room, the first thing Prof. Dr. Kaladji does is connect his USB stick to the EndoNaut. This is how he accesses and displays the EndoSize planning data on the screens of the Therenva system. In the next step, he uses the Ziehm Vision RFD Hybrid Edition CMOSline to see the locations of the vessel occlusions that he already saw on the CT image. He then starts the registration process, in which the CT image automatically adapts to the section of the live image. As soon as Prof. Dr. Kaladji confirms the image fusion on the EndoNaut touch panel, a blue vessel overlay including the points marked in EndoSize is displayed on the live image. To ensure that the vessel overlay is displayed in the correct location, Prof. Dr. Kaladji performs a control angiography with a small amount of contrast agent using the C‑arm. Once he is satisfied with the position of the overlay, he can place the stents at the marked locations. He uses the Ziehm Vision RFD Hybrid Edition CMOSline to monitor progress. Once the stents are placed, Prof. Dr. Kaladji checks the result at the end of the procedure with the C‑arm.


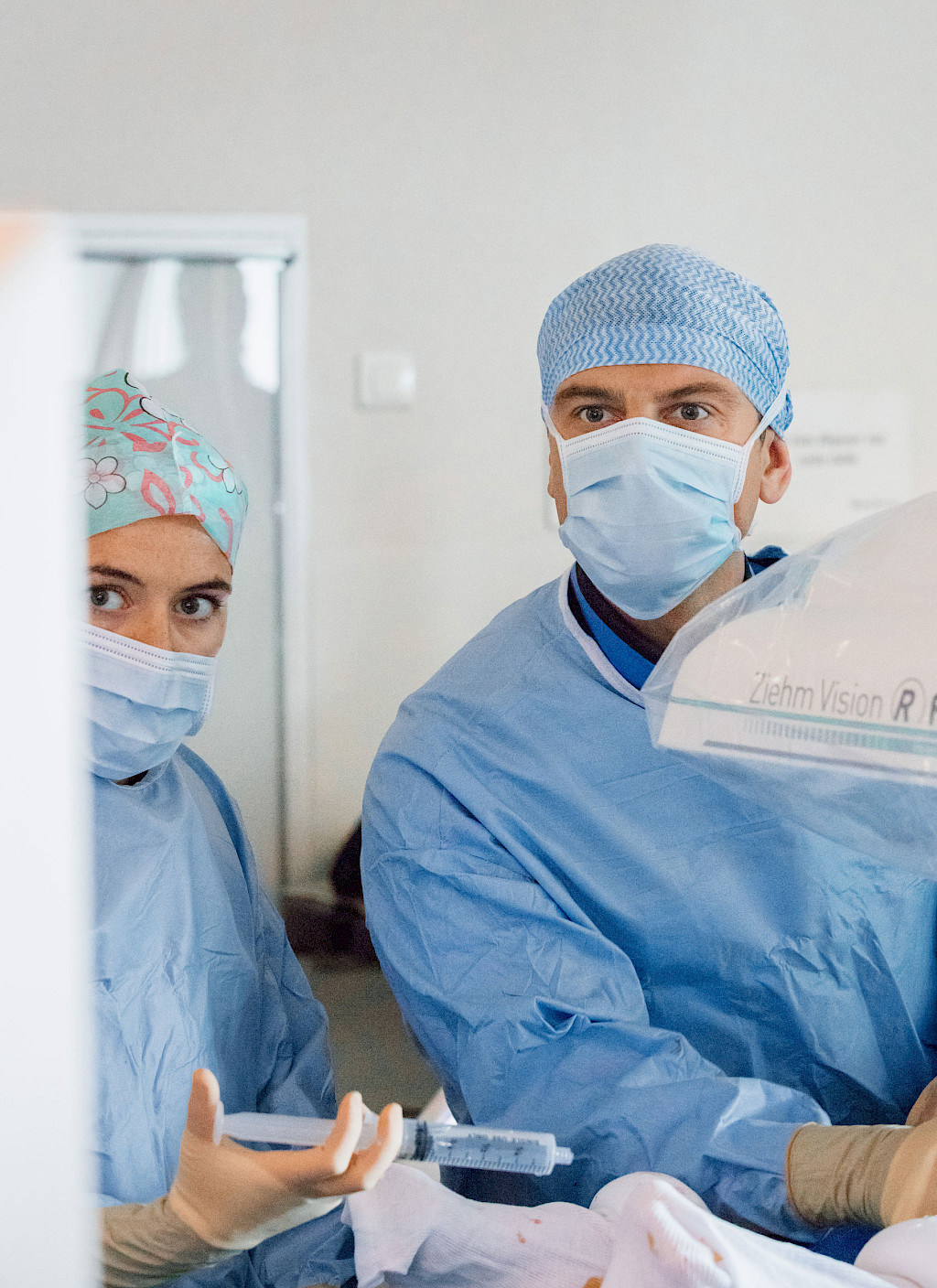
The combination of pre-planned surgical data and its fusion with live images during surgery is a tremendous advance in medical imaging for the vascular surgeon. “Before the combination of Ziehm Imaging and Therenva systems, we were well-acquainted with the really good imaging and intuitive handling of Ziehm’s mobile C‑arm for surgeons. Now we are reaping the benefits of being able to combine world-class 2D imaging with a 3D imaging environment. We have used many different C‑arms, but Ziehm Imaging’s mobile C‑arm was the best even before we started using it with Therenva’s EndoNaut. And EndoNaut is very helpful for surgeons. The systems complement each other perfectly.”
Prof. Dr. Kaladji sees the advantages of image fusion for other fields as well: “In the future, image fusion will also be important for cardiologists, especially for TAVI interventions, for example,” says Prof. Dr. Kaladji. TAVI stands for ‘transcatheter aortic valve implantation.’ In this procedure, the biological heart valve prosthesis is implanted using a minimally invasive method. Prof. Dr. Kaladji is convinced “that image fusion will be as useful to surgeons in cardiology as it is to me in vascular surgery.”
Disclaimer
1
EndoSize® is a registered trademark of Therenva SAS. In the USA, the EndoSize® software obtained a substantial equivalence determination and FDA clearance through the CDRH premarket notification process (510(K)). In Europe, the EndoSize® software is CE marked (class IIa), not eligible for reimbursement. The information provided in the labelling and manual is intended for healthcare professional.
2
EndoNaut® is a registered trademark of Therenva SAS. In the USA, the EndoNaut® software obtained a substantial equivalence determination and FDA clearance through the CDRH premarket notification process (510(K)). In Europe, the EndoNaut® software is CE marked (class IIb), not eligible for reimbursement. The information provided in the labelling and manual is intended for healthcare professionals only. For the safe and successful operation and use of the device, always read the instructions.
3
Ziehm Vision RFD Hybrid Edition represents a group of optional hardware and software that creates an option package on the device named Ziehm Vision RFD.
4
CMOSline represents a system configuration that is based on a Ziehm Imaging CMOS flat-panel detector.
More information on the University Hospital in Rennes (in French)
More information on Ziehm Vision RFD Hybrid Edition
More information on EndoNaut
More information on EndoSize
—
This clinical story was published in issue 5 (2022).
Download issue 5 as PDF